Option greeks explained
Options represent the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specified strike price. Each option has an expiration date and a premium (its price), which is determined by an options pricing model that reflects the underlying risk factors. Option Greeks provide insight into these risks by quantifying how each factor affects an option’s value. By combining these metrics with an options pricing model, traders gain a clearer view of the price fluctuations and risk profile associated with options.
Types of options greek
The Greeks help traders manage and anticipate changes in option prices, with each Greek focusing on a different aspect of sensitivity:
1. Option greek delta
Delta gauges the sensitivity of an option's price to a one-point change in the price of the underlying asset. For call options, delta values range from 0 to 1, while for put options, they range from -1 to 0. A delta nearing 1 (or -1 for puts) suggests that the option price will move almost identically with the underlying asset. Delta is also indicative of the likelihood that an option will end up in-the-money.
2. Gamma options greek
Gamma measures how quickly an option's delta changes as the underlying asset's price changes. It helps traders understand the stability of an option's delta, with a high gamma indicating the potential for rapid changes in the delta even with minor price movements in the underlying asset. This is particularly important for traders managing delta hedging strategies.
3. Option greek vega
Vega quantifies an option's price sensitivity to changes in the volatility of the underlying asset. It shows the expected price change of an option for a 1% change in implied volatility. Vega becomes especially relevant in volatile markets, as increased uncertainty typically leads to higher option prices. Vega is unique as it is not represented by a Greek letter.
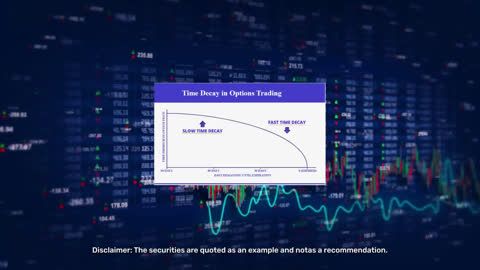
4. Theta option greeks
Theta signifies the rate of decline in an option's value over time, a concept known as time decay. It estimates how much an option's price will decrease each day, all else being equal. Theta's importance grows as the option's expiration date draws closer, emphasising the time-sensitive nature of options.
5. Rho option greeks
Rho calculates an option's price sensitivity to changes in the risk-free interest rate. It estimates how much an option's price could change with a 1% shift in interest rates. Although Rho is often less scrutinised than the other greeks in options trading, it can gain importance in scenarios of fluctuating interest rates.
Additional Read: F and O Trading
Importance of option greeks
Option Greeks are essential tools for making informed decisions in options trading. They help traders understand risk management and pricing strategies. By including the Greeks in their arsenal, investors can effectively analyse how different factors can potentially affect their options positions.
For instance, delta shows how the price of an option changes in relation to the underlying asset, aiding traders in assessing the scope of potential rewards and associated risks in a position. Gamma reveals how quickly delta changes, indicating the sensitivity of an option to price shifts in the underlying asset. Other Greeks like vega, rho and theta also play crucial roles in understanding options pricing. They enable traders to make well-informed decisions based on risk tolerance and prevailing market conditions.
Understanding and using Option Greeks can greatly improve a trader’s success in options trading.
Role of option greeks
Most prominently, Option Greeks are a major component of speculative strategy crafting and portfolio hedging. They are used to understand and analyse the various potential risks to an options portfolio.
As a popular example, one of the Greeks, delta, is used to determine how sensitive an option’s price is in relation to changes in the price of the underlying asset. This empowers traders to craft hedging strategies for their position. This also encourages portfolio diversification to safeguard against market volatility, which can be achieved by adjusting position sizes.
Besides delta, other Greeks like vega and gamma also help traders adjust their strategies by modifying positions and their sizes. Gamma shows how quickly delta changes, helping traders adjust to market movements, and vega indicates how changes in implied volatility can affect option prices.
Conclusion
For participants in the securities market, a thorough understanding of option greeks is invaluable for managing the risks associated with options trading. By mastering delta, gamma, vega, theta, and rho, traders and investors can make more informed decisions, effectively hedge their positions, and refine their investment strategies. While the greeks may seem complex at first, their application can significantly improve the risk management and performance of an options portfolio. Their use should complement a broader strategy that includes a deep understand ding of market conditions and a thoughtful trading approach.
Related Articles
What is Option Chain in NSE?
What is an index option?
What are the options Chain?
What is a Stock Option?
What is short selling?